3S-HMGB1, LPS-Free
HMGB1 is a nuclear protein that is released passively by necrotic cells, retained by apoptotic cells, and secreted actively by inflammatory cells (Dumitriu et al. HMGB1: guiding immunity from within. Trends Immunol 2005, 26: 381-7). HMGB1 is essential for life: Hmgb1 knockout mice die shortly after birth.
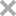
HMGB1 contains three conserved cysteine residues (C23, C45 and C106) and is a redox-sensitive (Yang et al, 2012). Chemotaxis-HMGB1 (the form with chemoattractanct activity) is completely reduced; cytokine-HMGB1 contains a disulfide bond between C23 and C45; further oxidation to sulfonates abrogate both activities.
In 3S-HMGB1 all cysteines are replaced with serines: these replacements preserve chemoattractant activity in vitro and in vivo, eliminate the cytokine-inducing activity and make the protein resistant to inactivation by ROS (Venereau et al, 2012). The mutant protein is produced in E. coli.
It has the sequence:
[“MGKGDPKKPR GKMSSYAFFV QTSREEHKKK HPDASVNFSE FSKKSSERWK TMSAKEKGKF EDMAKADKAR YEREMKTYIP PKGETKKKFK DPNAPKRPPS AFFLFSSEYR PKIKGEHPGL SIGDVAKKLG EMWNNTAADD KQPYEKKAAK LKEKYEKDIA AYRAKGKPDA AKKGVVKAEK SKKKKEEEDD EEDEEDEEEE EEEEDEDEEE DDDDE”]
Molecular Mass: Non-oxidizable chemokine-HMGB1 consists of 215 amino acid residues and has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 24.8 kDa.
Structure: HMGB1 consists of two fairly rigid, L-shaped DNA-binding domains, each referred to as a ‘HMG box’, and an unstructured tail that ends with 30 consecutive negatively charged amino acids.
Purity: The purified protein is >95% homogeneous (electrophoresis). It contains no nucleic acids.
Endotoxin Level: The purified protein is free from LPS (Pierce™ Chromogenic Endotoxin Quant Kit, <0.1 EU/mL). The product contains <0.006% v/v of Triton X-114 due to LPS removal procedure. The remaining traces of Triton X-114 can be removed upon request.
Activity: Measured by its ability to induce cell migration. Maximal activity in the cell migration assay is obtained at 1 nM.
Buffer & Reconstitution: the lyophilized protein once reconstituted with distilled water will be dissolved in a solution containing 50 mM HEPES pH 7.9, 500 mM NaCl.
Storage: 2-8°C. The protein once resuspended can be stored frozen (-20°C).This product is intended for research only, and cannot be used on humans.
This product is intended for research only, and cannot be used on humans.
Publications:
- An 8-Hydroxy-Quinoline Derivative Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lethality in Endotoxemia by Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Caspase-11 Signaling
- Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Canine Platelets Upregulate High Mobility Group Box-1 via Toll-Like Receptor 4
- A RAGE-antagonist peptide potentiates polymeric micelle-mediated intracellular delivery of plasmid DNA for acute lung injury gene therapy
- The Time-Course of Antioxidant Irisin Activity: Role of the Nrf2/HO-1/HMGB1 Axis
- Lipopolysaccharide-regulated secretion of soluble and vesicle-based proteins from a panel of colorectal cancer cell lines
- High-mobility group box protein-1 induces acute pancreatitis through activation of neutrophil extracellular trap and subsequent production of IL-1β
- Increased cell-free fetal DNA release after apoptosis and sterile inflammation in human trophoblast cells
- Photodynamic Therapy in Combination with the Hepatitis B Core Virus-like Particles (HBc VLPs) to Prime Anticancer Immunity for Colorectal Cancer Treatment
- The protective mechanism of salidroside modulating miR-199a-5p/TNFAIP8L2 on lipopolysaccharide-induced MLE-12 cells
- Inhibition of inflammatory liver injury by the HMGB1-A box through HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB signaling in an acute liver failure mouse model
- Association of High Mobility Group Box-Protein 1 and Platelet Microparticles in Patients After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- HMGB1 Release Induced by EV71 Infection Exacerbates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption via VE-cadherin Phosphorylation
- [Altered expression of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps]
- HMGB1 induces hepcidin upregulation in astrocytes and causes an acute iron surge and subsequent ferroptosis in the postischemic brain
- HMGB1-activated tumor-associated macrophages promote migration and invasion via NF-κB/IL-6 signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- The Expression of High Mobility Group Box-1 (HMG1) in the Peripheral Blood and Its Relation with Systemic Vasculitis Patients
- The translational potential of miR-26 in atherosclerosis and development of agents for its target genes ACC1/2, COL1A1, CPT1A, FBP1, DGAT2, and SMAD7
- HMGB1 cleavage by complement C1s and its potent anti-inflammatory product
- HMGB1 Promotes the Release of Sonic Hedgehog From Astrocytes
- Aberrant phase separation and nucleolar dysfunction in rare genetic diseases
- Serum sirtuin-1 a potential marker in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis
- Apoptotic cell death in disease-Current understanding of the NCCD 2023
- Optogenetic cortical spreading depolarization induces headache-related behaviour and neuroinflammatory responses some prolonged in familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 mice
- Npro of classical swine fever virus enhances HMGB1 acetylation and its degradation by lysosomes to evade from HMGB1-mediated antiviral immunity
- Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for the biosynthesis of geraniol
- HMGB1 promotes chemoresistance in small cell lung cancer by inducing PARP1-related nucleophagy
- The HMGB1 (C106A) mutation inhibits IL-10-producing CD19hiFcγRIIbhi B cell expansion by suppressing STAT3 activation in mice
- The Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 in Ischemic Stroke
- Nonoxid-HMGB1 Attenuates Cognitive Impairment After Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats
- The Anti-inflammatory Effects of HMGB1 Blockades in a Mouse Model of Cutaneous Vasculitis
- HMGB1: A Common Biomarker and Potential Target for TBI, Neuroinflammation, Epilepsy, and Cognitive Dysfunction
- The Roles of High Mobility Group Box 1 in Cerebral Ischemic Injury
- Toxoplasma gondii Infection Induces High Mobility Group Box 1 Released from Mouse Macrophages
- Impact of folic acid supplementation on ischemia‒reperfusion-induced kidney injury in rats: folic acid prophylactic role revisited
- Co-existence of anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase-65 and anti-sry-like high-mobility group box receptor antibody-associated autoimmune encephalitis: A rare case report
- High Mobility Group Box 1 Gene Polymorphism and Serum High Mobility Group Box 1, Interleukin 1 Beta, and Alpha-Klotho Crosstalk in Severe COVID-19 Patients
- HO-1 attenuates testicular ischaemia/reperfusion injury by activating the phosphorylated C-jun-miR-221/222-TOX pathway
- MicroRNA-146a gene transfer ameliorates senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotypes in tendinopathic tenocytes
- Therapeutic effects of anti-diabetic drugs on traumatic brain injury
- ASSOCIATION BETWEEN HIGH MOBILITY GROUP BOX 1 PROTEIN GENE (rs41369348) POLYMORPHISM AND IMMUNOGLOBULIN A VASCULITIS IN CHILDREN
- Venereau et al (2012) Mutually exclusive redox forms of HMGB1 promote cell recruitment or proinflammatory cytokine release. Journal of Experimental Medicine (2012).
- Tirone et al (2017) High mobility group box 1 orchestrates tissue regeneration via CXCR4. J.Exp Med
 Download 3S-HMGB1 Datasheet
Download 3S-HMGB1 Datasheet
Complete Name: High Mobility Group 1 Mutant
Other Names: 3S, Amphoterin-1, High mobility group protein 1 mutant ,3S Mutant, Triple Serine Mutant, HMG-1, SBP-1, high-mobility group box 1, Amphoterin, HMG1, recombinant HMGB1


![Hmgb1 knock out MEF Large T antigen [HM-201]](https://www.hmgbiotech.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/4-500x500.png)