SDF1 – Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1α ( CXCL12) tested in migration, LPS-Free
Recombinant Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1α (SDF-1α) is a 8 kDa chemokine protein expressed in many tissues and cell types.
The protein is almost identical (92% homology) in human, mouse and rat.
The chemokine SDF-1α binds to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and plays an essential and unique role in homeostatic regulation of leukocyte traffic, hematopoiesis, organogenesis, cell differentiation and tissue regeneration (Murphy, 2002).
SDF-1α forms an heterocomplex with the alarmin HMGB1 (High Mobility Group 1) to promote the recruitment of cells via CXCR4 receptor.
It has the sequence:
[“MKPVSLSYRCPCRFFESHVARANVKHLKILNTPNCALQIVARLKNNNRQVCIDPKLKWIQEYLEKALNK”]
Molecular Mass: Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1α (SDF-1α, CXCL12) consists of 69 amino acid residues and has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 8 kDA
Purity: The purified protein is >95% homogeneous (electrophoresis). It contains no nucleic acids.
Endotoxin Level: The purified protein is free from LPS (Pierce™ Chromogenic Endotoxin Quant Kit, <0.1 EU/mL). The product contains <0.006% v/v of Triton X-114 due to LPS removal procedure. The remaining traces of Triton X-114 can be removed upon request.
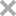
Activity: Measured by its ability to induce migration. Maximal activity in the cell migration assay is obtained at 1 nM.
Buffer & Reconstitution: the lyophilized protein once reconstituted with distilled water will be dissolved in a solution of DPBS without Ca and Mg.
Storage: 2-8°C when lyophilized. The protein once reconstituted with water can be stored frozen (-20°C). Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
This product is intended for research only, and cannot be used on humans.
Publications:
- An 8-Hydroxy-Quinoline Derivative Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lethality in Endotoxemia by Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Caspase-11 Signaling
- Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Canine Platelets Upregulate High Mobility Group Box-1 via Toll-Like Receptor 4
- A RAGE-antagonist peptide potentiates polymeric micelle-mediated intracellular delivery of plasmid DNA for acute lung injury gene therapy
- The Time-Course of Antioxidant Irisin Activity: Role of the Nrf2/HO-1/HMGB1 Axis
- Lipopolysaccharide-regulated secretion of soluble and vesicle-based proteins from a panel of colorectal cancer cell lines
- High-mobility group box protein-1 induces acute pancreatitis through activation of neutrophil extracellular trap and subsequent production of IL-1β
- Increased cell-free fetal DNA release after apoptosis and sterile inflammation in human trophoblast cells
- Photodynamic Therapy in Combination with the Hepatitis B Core Virus-like Particles (HBc VLPs) to Prime Anticancer Immunity for Colorectal Cancer Treatment
- The protective mechanism of salidroside modulating miR-199a-5p/TNFAIP8L2 on lipopolysaccharide-induced MLE-12 cells
- Inhibition of inflammatory liver injury by the HMGB1-A box through HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB signaling in an acute liver failure mouse model
- CXCL12 promotes the crossing of retinal ganglion cell axons at the optic chiasm
- Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction promotes PDGF-primed bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for myocardial protection in acute Myocardial Infarction in rats
- Biodegradable nano black phosphorus based SDF1-α delivery system ameliorates Erectile Dysfunction in a cavernous nerve injury rat model by recruiting endogenous stem/progenitor cells
- Methazolamide Reduces the AQP5 mRNA Expression and Immune Cell Migration-A New Potential Drug in Sepsis Therapy?
- Correlations of Serum Retinol-Binding Protein and Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 with Renal Function in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease
- RNA Analysis of Circulating Leukocytes in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease
- Suggested mechanism of CCR5Δ32, CCR2-64I and SDF 1-3’A allele frequency change in Polish and Lithuanian gene pools from the perspective of passing time
- Molecular and Brain Volume Changes Following Aerobic Exercise, Cognitive and Combined Training in Physically Inactive Healthy Late-Middle-Aged Adults: The Projecte Moviment Randomized Controlled Trial
- Secondary damage and neuroinflammation in the spinal dorsal horn mediate post-thalamic hemorrhagic stroke pain hypersensitivity: SDF1-CXCR4 signaling mediation
- SDF1-CXCR4 Signaling Maintains Central Post-Stroke Pain through Mediation of Glial-Neuronal Interactions
- The importance of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in therapeutic approaches to Diabetes mellitus attenuation
- Peroxynitrite Exposure of CXCL12 Impairs Monocyte, Lymphocyte and Endothelial Cell Chemotaxis, Lymphocyte Extravasation in vivo and Anti-HIV-1 Activity
- Upregulation of C-X-C motif chemokine 12 in the spinal cord alleviated the symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats
- Disruption of placental ACKR3 impairs growth and hematopoietic development of offspring
- Study on the mechanism of CXCL12/CXCR4-axis-mediated upregulation of IL-8 and IL-6 on the biological function of acute T lymphocyte leukaemia cells
- CXCL12-CXCR4 mediates CD57+ CD8+ T cell responses in the progression of type 1 diabetes
- Zebrafish tsc1 and cxcl12a increase susceptibility to mycobacterial infection
- Advance in the role of chemokines/chemokine receptors in carcinogenesis: Focus on pancreatic cancer
- Combined bioinformatics and machine learning methodologies reveal prognosis-related ceRNA network and propose ABCA8, CAT, and CXCL12 as independent protective factors against osteosarcoma
- Single-cell analysis reveals alterations in cellular composition and cell-cell communication associated with airway inflammation and remodeling in asthma
16th June 2023
HMGB1●CXCL12 : the first fuzzy chemokines heterocomplex reported so far
HMGBiotech Srl participated in a recent study in which, through an integrative structural approach,
approach,
molecular details of HMGB1●CXCL12 heterocomplex formation were unveiled.
This dynamic complex is formed equimolarly, contrary to previous assumptions.
Structured and unstructured HMGB1 regions interact with the dimerization surface of CXCL12. This work elucidated how the acidic IDR is involved in HMGB1●CXCL12 complex formation.The findings suggest that interfering with the interactions in the HMGB1●CXCL12 complex could potentially inhibit its detrimental effects in inflammatory conditions. Read the full article about the study…
Mantonico et al. The acidic intrinsically disordered region of the inflammatory mediator HMGB1 mediates fuzzy interactions with chemokine CXCL12. bioRxiv 2023.
References:
Schiraldi et al (2012) HMGB1 promotes recruitment of inflammatory cells to damaged tissues by forming a complex with CXCL12 and signaling via CXCR4. J Exp Med. 2012: 551–563.


![Hmgb1 knock out MEF 3T3 method [HM-221]](https://www.hmgbiotech.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/4-500x500.png)