Fully reduced HMGB1, LPS-Free
HMGB1 is a nuclear protein that is released passively by necrotic cells, retained by apoptotic cells, and secreted actively by inflammatory cells.
HMGB1 is essential for life: Hmgb1 knockout mice die shortly after Birth (Dumitriu et al. HMGB1: guiding immunity from within. Trends Immunol 2005, 26: 381-7).
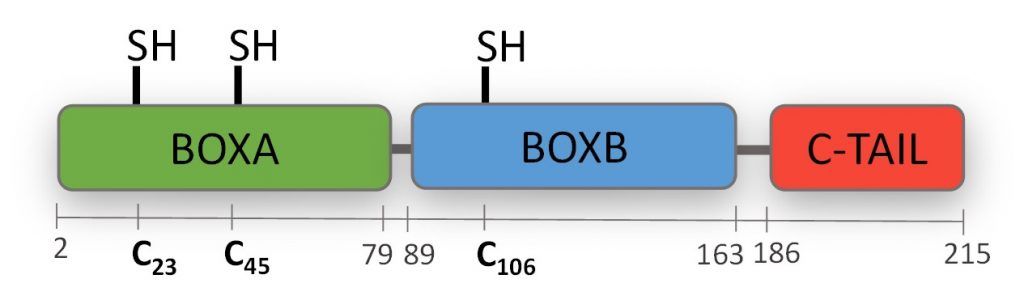
The two different activities of HMGB1 as a chemoattractanct of motile cells and as inducer of cytokines have been attributed to different biochemical forms. Fully reduced HMGB1 complete notation: HMGB1C23hC45hC106h – Antoine J.,2014) is completely reduced and has chemoattractanct activity; Disulfide HMGB1 contains a disulfide bond between C23 and C45 (complete notation: HMGB1C23-C45C106h – Antoine J.,2014) and can induce cytokine and chemokine production in monocytes and other inflammatory cells.
Fully reduced HMGB1 had previously been sold by HMGBiotech as Chemotaxis-HMGB1 LPS free and tested in migration assay, but is otherwise the same identical product.
Fully reduced HMGB1 behaves as a trigger of inflammation, attracting inflammatory cells, and of tissue repair, attracting stem cells and promoting their proliferation. Moreover, Fully reduced HMGB1 activates dedritic cells and promotes their functional maturation and migration to lymph nodes.
However, and contrary to early reports, pure Fully reduced HMGB1 does not promote cytokine secretion. Cytokine secretion is only promoted by disulfide HMGB1 (the form containing disulfide bond).
The Fully reduced HMGB1 we provide is the natural protein, with no tags or additional amino acids. It is produced in E.coli from an expression plasmid coding for the human protein.
It has the sequence:
[“MGKGDPKKPR GKMSSYAFFV QTCREEHKKK HPDASVNFSE FSKKCSERWK TMSAKEKGKF EDMAKADKAR YEREMKTYIP PKGETKKKFK DPNAPKRPPS AFFLFCSEYR PKIKGEHPGL SIGDVAKKLG EMWNNTAADD KQPYEKKAAK LKEKYEKDIA AYRAKGKPDA AKKGVVKAEK SKKKKEEEDD EEDEEDEEEE EEEEDEDEEE DDDDE” ]
Molecular Mass: HMGB1 consists of 215 amino acid residues and has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 24.8 kDa. It migrates at a position of approximately 30 kD in SDS-PAGE gels, possibly because of the unusual number of positively charged amino acids it contains.
Structure: HMGB1 consists of two fairly rigid, L-shaped DNA-binding domains, each referred to as a ‘HMG box’, and an unstructured tail that ends with 30 consecutive negatively charged amino acids.
Species specificity: the sequence and structure of HMGB1 have been strictly conserved during evolution, and HMGB1 proteins from all mammals are almost identical (Sessa L, Bianchi ME. The evolution of High Mobility Group Box (HMGB) chromatin proteins in multicellular animals. Gene 2007, 387:133-40).
Purity: The purified protein is >95% homogeneous (electrophoresis and mass spectrometry). It contains no nucleic acids, nor IL-1beta.
Endotoxin Level: The purified protein is free from LPS (Cambrex Limulus Amoebocyte Assay QCL-1000, <0.4 ng LPS per mg protein).
Activity: Measured by its ability to induce migration. Maximal activity in the cell migration assay is obtained at 1 nM, or 25 ng/ml (Palumbo et al. Extracellular HMGB1, a signal of tissue damage, induces mesoangioblast migration and proliferation. J Cell Biol 2004, 164: 441-9).
Buffer: 50 mM HEPES-Na pH 7.9, 500 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM DTT.
Storage: the protein is shipped lyophilized. Once resuspended can be stored frozen at -20°C. To avoid cysteine oxidation, DTT 0.5mM is added during protein purification.
This product is intended for research only, and cannot be used on humans.
Publications:
- An 8-Hydroxy-Quinoline Derivative Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lethality in Endotoxemia by Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Caspase-11 Signaling
- Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Canine Platelets Upregulate High Mobility Group Box-1 via Toll-Like Receptor 4
- A RAGE-antagonist peptide potentiates polymeric micelle-mediated intracellular delivery of plasmid DNA for acute lung injury gene therapy
- The Time-Course of Antioxidant Irisin Activity: Role of the Nrf2/HO-1/HMGB1 Axis
- Lipopolysaccharide-regulated secretion of soluble and vesicle-based proteins from a panel of colorectal cancer cell lines
- High-mobility group box protein-1 induces acute pancreatitis through activation of neutrophil extracellular trap and subsequent production of IL-1β
- Increased cell-free fetal DNA release after apoptosis and sterile inflammation in human trophoblast cells
- Photodynamic Therapy in Combination with the Hepatitis B Core Virus-like Particles (HBc VLPs) to Prime Anticancer Immunity for Colorectal Cancer Treatment
- The protective mechanism of salidroside modulating miR-199a-5p/TNFAIP8L2 on lipopolysaccharide-induced MLE-12 cells
- Inhibition of inflammatory liver injury by the HMGB1-A box through HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB signaling in an acute liver failure mouse model
- Association of High Mobility Group Box-Protein 1 and Platelet Microparticles in Patients After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- HMGB1 Release Induced by EV71 Infection Exacerbates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption via VE-cadherin Phosphorylation
- [Altered expression of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps]
- HMGB1 induces hepcidin upregulation in astrocytes and causes an acute iron surge and subsequent ferroptosis in the postischemic brain
- HMGB1-activated tumor-associated macrophages promote migration and invasion via NF-κB/IL-6 signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- The Expression of High Mobility Group Box-1 (HMG1) in the Peripheral Blood and Its Relation with Systemic Vasculitis Patients
- The translational potential of miR-26 in atherosclerosis and development of agents for its target genes ACC1/2, COL1A1, CPT1A, FBP1, DGAT2, and SMAD7
- The Anti-inflammatory Effects of HMGB1 Blockades in a Mouse Model of Cutaneous Vasculitis
- HMGB1 cleavage by complement C1s and its potent anti-inflammatory product
- HMGB1 Promotes the Release of Sonic Hedgehog From Astrocytes
- The Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 in Ischemic Stroke
- Oxidation of HMGB1 Is a Dynamically Regulated Process in Physiological and Pathological Conditions
- Irradiation-Induced Changes in the Immunogenicity of Lung Cancer Cell Lines: Based on Comparison of X-rays and Carbon Ions
- Evidence for SIRT1 Mediated HMGB1 Release From Kidney Cells in the Early Stages of Hemorrhagic Shock
- Ginseng (Panax ginseng) leaf extract modulates the expression of heme oxygenase-1 to attenuate osteoclast differentiation
- C5a/C5aR1 axis as a key driver promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in airway epithelial cells in silica nanoparticles-induced pulmonary fibrosis
- Cisplatin Dependent Secretion of Immunomodulatory High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) Protein from Lung Cancer Cells
- HMGB1-RAGE axis contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulation of cardiomyocyte autophagy and apoptosis in diabetic mice
- Revolutionizing fracture fixation in diabetic and non-diabetic rats: High mobility group box 1-based coating for enhanced osseointegration
- Xiaobanxia decoction alleviates chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting by inhibiting GSDME-mediated pyroptosis
- Biological Effects of New Titanium Surface Coatings Based on Ionic Liquids and HMGB1: A Cellular and Molecular Characterization in Lewis Rats
- High mobility group A proteins as tumor markers
- High Mobility Group Proteins in Sepsis
- The Roles of High Mobility Group Box 1 in Cerebral Ischemic Injury
- MiR-2113 overexpression attenuates sepsis-induced acute pulmonary dysfunction, inflammation and fibrosis by inhibition of HMGB1
- Transposon dynamics in the emerging oilseed crop Thlaspi arvense
- Comparative analyses of the Smith-Magenis syndrome protein RAI1 in mice and common marmoset monkeys
- Intestinal epithelia and myeloid immune cells shape colitis severity and colorectal carcinogenesis via High-mobility group box protein 1
- Toxoplasma gondii Infection Induces High Mobility Group Box 1 Released from Mouse Macrophages
- Impact of folic acid supplementation on ischemia‒reperfusion-induced kidney injury in rats: folic acid prophylactic role revisited
- Co-existence of anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase-65 and anti-sry-like high-mobility group box receptor antibody-associated autoimmune encephalitis: A rare case report
- High Mobility Group Box 1 Gene Polymorphism and Serum High Mobility Group Box 1, Interleukin 1 Beta, and Alpha-Klotho Crosstalk in Severe COVID-19 Patients
- HO-1 attenuates testicular ischaemia/reperfusion injury by activating the phosphorylated C-jun-miR-221/222-TOX pathway
- MicroRNA-146a gene transfer ameliorates senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotypes in tendinopathic tenocytes
- Therapeutic effects of anti-diabetic drugs on traumatic brain injury
- ASSOCIATION BETWEEN HIGH MOBILITY GROUP BOX 1 PROTEIN GENE (rs41369348) POLYMORPHISM AND IMMUNOGLOBULIN A VASCULITIS IN CHILDREN
- Limana et al. Exogenous High-Mobility Group Box 1 protein induces myocardial regeneration following infarction via enhanced cardiac c-kit cell proliferation and differentiation. Circ Res 2005, 97:73-83.
- Other publications: 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10, 11 , 12
16th June 2023
HMGB1●CXCL12 : the first fuzzy chemokines heterocomplex reported so far
HMGBiotech Srl participated in a recent study in which, through an integrative structural approach,
approach,
molecular details of HMGB1●CXCL12 heterocomplex formation were unveiled.
This dynamic complex is formed equimolarly, contrary to previous assumptions.
Structured and unstructured HMGB1 regions interact with the dimerization surface of CXCL12. This work elucidated how the acidic IDR is involved in HMGB1●CXCL12 complex formation.The findings suggest that interfering with the interactions in the HMGB1●CXCL12 complex could potentially inhibit its detrimental effects in inflammatory conditions. Read the full article about the study…
Mantonico et al. The acidic intrinsically disordered region of the inflammatory mediator HMGB1 mediates fuzzy interactions with chemokine CXCL12. bioRxiv 2023.
 Download Fully reduced HMGB1 Datasheet
Download Fully reduced HMGB1 Datasheet
Complete Name: High Mobility Group 1
Other Names: Amphoterin-1, High mobility group protein 1,HMG-1, SBP-1, high mobility group protein B1, high-mobility group box 1, Amphoterin, HMG1, HMGB1, SBP-1, recombinant HMGB1





